

More specifically, modern roller chains exhibit high wear resistance, fatigue strength and tensile strength. Manufacturers make and assemble each of these subcomponents to precise tolerances and heat treat them to optimize performance. This type of chain consists of five basic components: pin, bushing, roller, pin link plate and roller link plate. Read the related article: What are Roller Chains? Technical SummaryĬhain-based machinery abounds, but the most common industrial designs use roller chain. Lower inset, the inner surface on the bushings in Tsubaki’s PerforMax chain has lubrication grooves to extend chain life. Tsubaki) shows the subcomponents in a chain linkage. Roller chain is an engineered power-transmission component. Remote installations benefit from long-life chain that requires no lubrication, for example. Now, advances in precision and technology let designers use chains in more applications than ever. They are versatile and reliable components to drive machinery and convey products. || Engineers have used chains in motion systems for more than a century.

Pal, S., Numerical Methods – Principles, Analyses, and Algorithms, Oxford University Press, New Delhi, India, pp.

261–278 (2012).Īckleh, A.S., Allen, E.J., Hearfott, R.B., and Seshaiyer, P., Classical and Modern Numerical Analysis – Theory, Methods and Practice, CRC Press, London, UK (2009). Gautschi, W., Numerical Analysis, 2nd Edition, Springer Publishing, New York, NY, pp. Greenbaum, A., and Chartier, T.P., Numeric Methods – Design, Analysis, and Computer Implementation of Algorithms, Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ, pp. Jianheng, X., The Calculation Method and Testing Technic of the Hy-vo Chain Shafting Center Distance, Jilin University, Changchun, China, pp. Xu, L., Ren, R., and Shi, Z.-h., “The Simulation Analysis of Chain Drive Polygon-effect Based on Pro/E,” Manufacturing Automation 31(5): 93–95 (2009). Zhang, L., Lu, T., and Luming, W., “Experimental Study on the Polygon-effect of Chain-transmission,” Mechanical Engineering & Automation 161(4): 97–99 (2010). Muhs, D., Wittel, H., Becker, M., Kong, J., (ed), Roloff/Matek Maschinenelemente, 16th Edition, China Machine Press, Beijing, China, pp.
CHAIN DRIVE PDF BASICS ISO
ISO 606:2004, “Short-pitch Transmission Precision Roller and Bush Chains, Attachments and Associated Chain Sprockets”. ISO 10823:2004, “Guidance on the Selection of Chain Drives”. Robert Bosch GmbH, Yuan, W.C., (ed), Automotive Handbook, 3rd Edition, Beijing Institute of Technology Press, Beijing, China, pp. Yabing, C., Fanzhong, M., Hanxue, X., and Jianming, W., “Experimental Study on High-speed Characteristic of Automotive Engine Oil-pump Chain,” Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering 20(1): 36–39 (2007).
CHAIN DRIVE PDF BASICS SERIES
Ward, A., and Dwyer-Joyce, R.S., “Model Experiments on Automotive Chain Drive Systems,” Tribology Series 39: 851–861 (2001).įanzhong, M., Shukun, W., Hong, L., Rongjin, X., and Hanxue, X., “Wear Failure Mechanism and Multi-impact Property of Automotive Engine Chain,” Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering 18(3): 401–404 (2005). ISO 9633:2001, “Cycle chains-Characteristics and test method”.īurgess, S.C., Pyper, T., and Ling, C.S., “A Linear Actuated Chain Test Rig Capable of Accelerated Test Speeds and Continuous Wear Measurements,” Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C: Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science 227: 1047–1055 (2013).
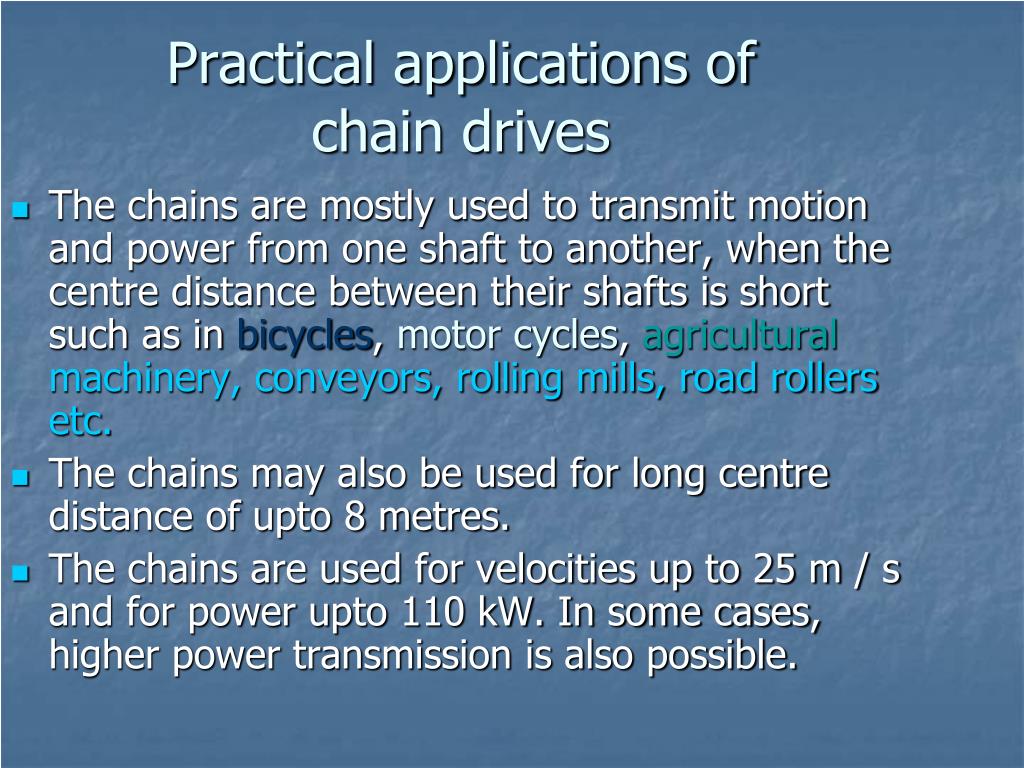
ISO 10190:1992, “Motor Cycle Chains-Characteristics and Test Methods”. ISO 1275:2006, “Double-Pitch Precision Roller Chains,Attachments and Associated Chain Sprockets for Transmission and Conveyors”. ISO 15654:2004, “Fatigue Test Method For Transmission Precision Roller Chain”.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
